| 产品名称 |
Recombinant Human BID |
| 英文名称 |
BID/BH3-interacting domain death agonist |
| 纯度 |
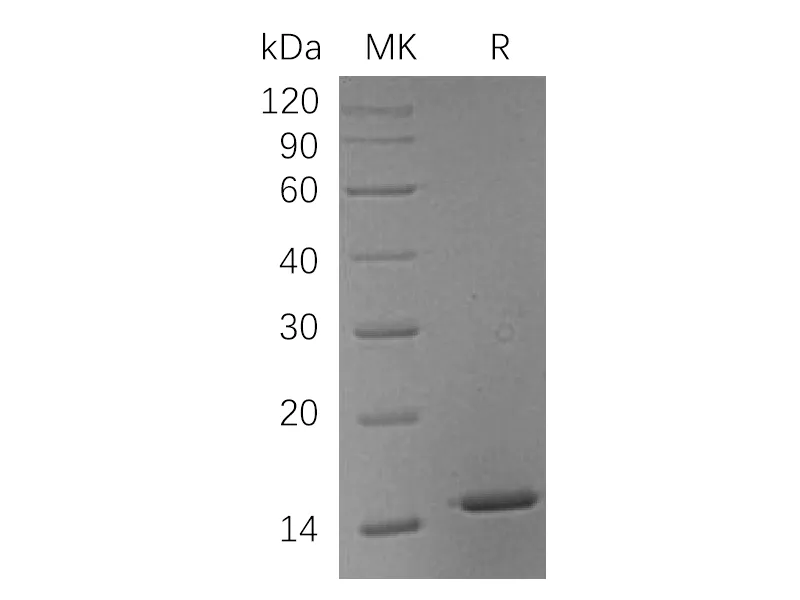
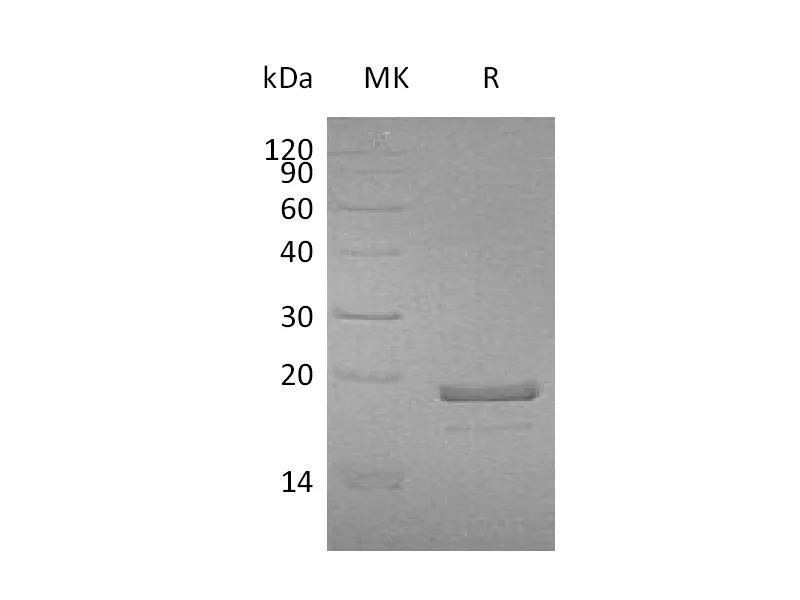
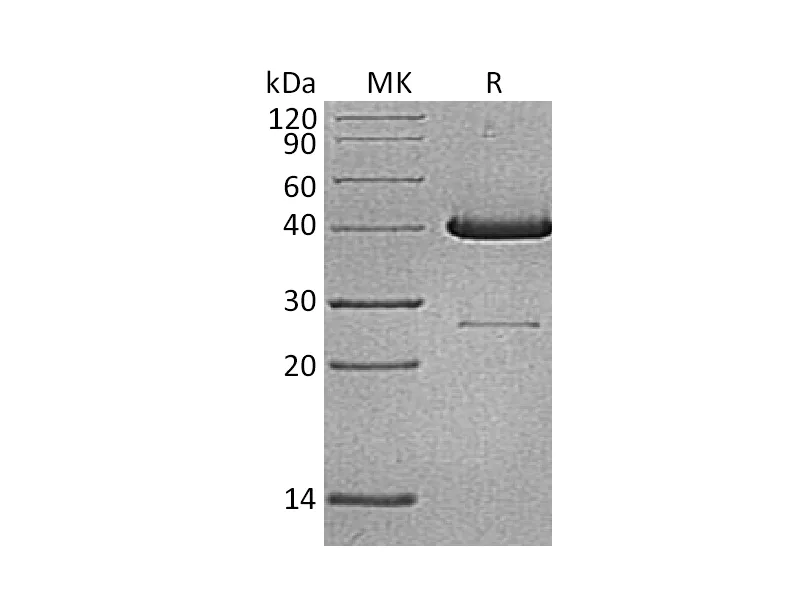
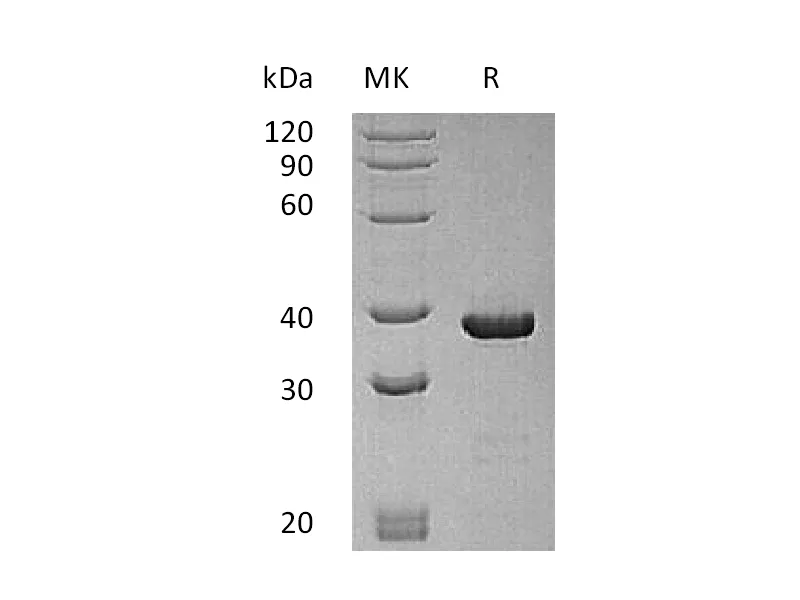
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 |
<1 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| 蛋白构建 |
Recombinant Human BH3-Interacting Domain Death Agonist is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Asp195 is expressed. |
| Accession |
P55957 |
| 表达宿主 |
E.coli |
| 种属 |
Human |
| 预测分子量 |
21.99 KDa |
| 制剂 |
Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB, 100mM KCl, pH 7.4. |
| 运输方式 |
The product is shipped on dry ice/polar packs.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| 稳定性&储存 |
Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 6 months after receipt.Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 3 months under sterile conditions after opening. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| 复溶 |
| 分子别名 |
| BH3-Interacting Domain Death Agonist; p22 BID; BID |
| 背景介绍 |
| BH3-Interacting Domain Death Agonist (BID) is a member of the Bcl-2 protein family which regulates outer mitochondrial membrane permeability. BID is a pro-apoptotic member that causes cytochrome c to be released from the mitochondria intermembrane space into the cytosol. Interaction of Bid with Bak causes altered mitochondrial membrane permeability. BID contains only the BH3 domain, which is required for its interaction with the Bcl-2 family proteins and for its pro-death activity. BID is susceptible to proteolytic cleavage by caspases, calpains, Granzyme B and cathepsins. It is an integrating key regulator of the intrinsic death pathway that amplifies caspase-dependent and caspase-independent execution of neuronal apoptosis. Therefore pharmacological inhibition of BID provides a promising therapeutic strategy in neurological diseases where programmed cell death is prominent, and also offer a new strategy for the treatment of acute renal failure associated with ischemia-reperfusion. BID receives direct inputs from a key regulator of the cell cycle arrest/DNA repair machinery (ATM), and therefore is an excellent candidate to coordinate genotoxic stress responses and apoptotic cell death. BID is a novel pro-apoptosis Bcl-2 family protein that is activated by caspase 8 in response to Fas/TNF-R1 death receptor signals. Deletion of BID inhibits carcinogenesis in the liver, although this genetic alteration promotes tumorigenesis in the myeloid cells. This is likely related to the function of BID to promote cell cycle progression into S phase. BID could be also involved in the maintenance of genomic stability by engaging at mitosis checkpoint. |
注意事项
本司产品仅用于科研,不用于临床诊断和治疗