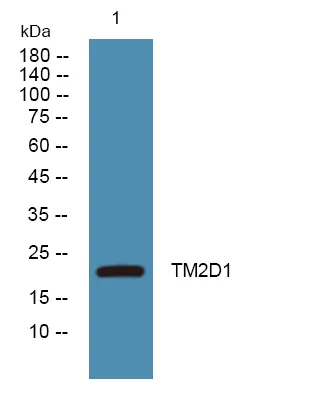
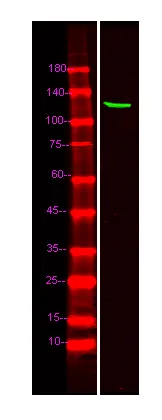
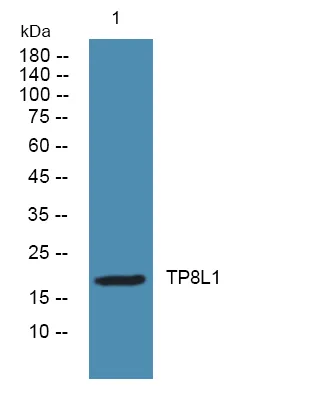
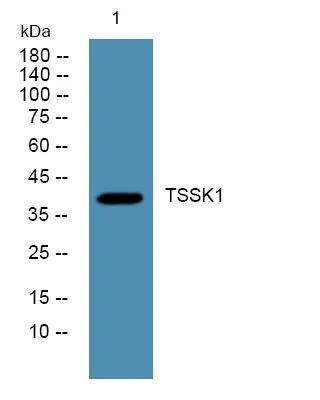
产品概述
产品性能
免疫原
产品应用
研究背景
The Bloom syndrome gene product is related to the RecQ subset of DExH box-containing DNA helicases and has both DNA-stimulated ATPase and ATP-dependent DNA helicase activities. Mutations causing Bloom syndrome delete or alter helicase motifs and may disable the 3'-5' helicase activity. The normal protein may act to suppress inappropriate recombination. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],disease:Defects in BLM are the cause of Bloom syndrome (BLM) [MIM:210900]. BLM is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by proportionate pre- and postnatal growth deficiency, sun-sensitive telangiectatic hypo- and hyperpigmented skin, predisposition to malignancy, and chromosomal instability.,function:Participates in DNA replication and repair. Exhibits a magnesium-dependent ATP-dependent DNA-helicase activity that unwinds single- and double-stranded DNA in a 3'-5' direction.,online information:BLM mutation db,PTM:Phosphorylated in response to DNA damage. Phosphorylation requires the FANCA-FANCC-FANCE-FANCF-FANCG protein complex, as well as the presence of RMI1.,similarity:Belongs to the helicase family. RecQ subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 helicase ATP-binding domain.,similarity:Contains 1 helicase C-terminal domain.,similarity:Contains 1 HRDC domain.,subunit:Part of the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC), which contains BRCA1, MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, ATM, BLM, PMS2 and the RAD50-MRE11-NBS1 protein complex. This association could be a dynamic process changing throughout the cell cycle and within subnuclear domains. Interacts with ubiquitinated FANCD2. Interacts with RMI complex. Interacts directly with RMI1 component of RMI complex.,
研究领域
Homologous recombination;