产品概述
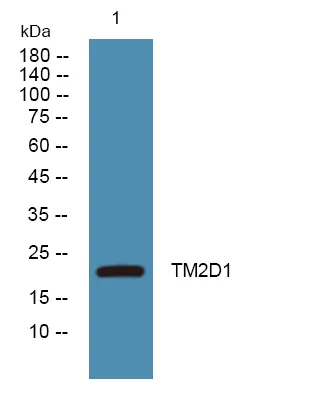
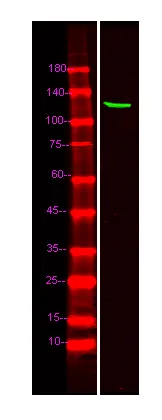
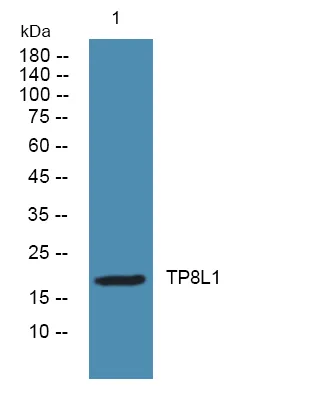
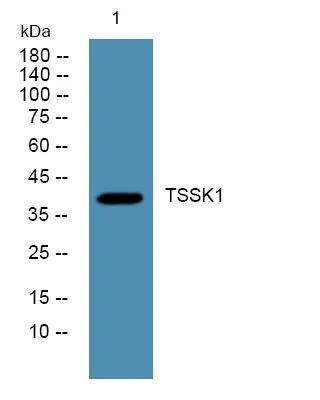
产品性能
免疫原
产品应用
研究背景
This gene encodes a tumor suppressor protein that acts as an antagonist of the Wnt signaling pathway. It is also involved in other processes including cell migration and adhesion, transcriptional activation, and apoptosis. Defects in this gene cause familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), an autosomal dominant pre-malignant disease that usually progresses to malignancy. Disease-associated mutations tend to be clustered in a small region designated the mutation cluster region (MCR) and result in a truncated protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],disease:APC mutations have led to some interesting observations. (1) the great majority of the mutations found to date would result in truncation of the APC product. (2) almost all the mutations have occurred within the first half of the coding sequence, and somatic mutations in colorectal tumors are further clustered in a particular region, called MCR (mutation cluster region). (3) most identified point mutations in the APC gene are transitions from cytosine to other nucleotides. (4) the location of germline mutations tends to correlate with the number of colorectal polyps in FAP patients. Inactivation of both alleles of the APC gene seems to be required as an early event to develop most adenomas and carcinomas in the colon and rectum as well as some of those in the stomach.,disease:Defects in APC are a cause of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) [MIM:175100]; which includes also Gardner syndrome (GS). FAP and GS contribute to tumor development in patients with uninherited forms of colorectal cancer. FAP is characterized by adenomatous polyps of the colon and rectum, but also of upper gastrointestinal tract (ampullary, duodenal and gastric adenomas). This is a viciously premalignant disease with one or more polyps progressing through dysplasia to malignancy in untreated gene carriers with a median age at diagnosis of 40 years.,disease:Defects in APC are a cause of hereditary desmoid disease (HDD) [MIM:135290]; also called familial infiltrative fibromatosis (FIF). It is an autosomal dominant trait with 100% penetrance and possible variable expression among affected relatives. HDD patients show multifocal fibromatosis of the paraspinal muscles, breast, occiput, arms, lower ribs, abdominal wall, and mesentery. Desmoid tumors appears also as a complication of familial adenomatous polyposis.,disease:Defects in APC are a cause of medulloblastoma (MDB) [MIM:155255]. MDB is a malignant, invasive embryonal tumor of the cerebellum with a preferential manifestation in children. Although the majority of medulloblastomas occur sporadically, some manifest within familial cancer syndromes such as Turcot syndrome and basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlin syndrome).,disease:Defects in APC are a cause of Turcot syndrome [MIM:276300]. Turcot syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by malignant tumors of the brain associated with multiple colorectal adenomas. Skin features include sebaceous cysts, hyperpigmented and cafe au lait spots.,function:Tumor suppressor. Promotes rapid degradation of CTNNB1 and participates in Wnt signaling as a negative regulator. APC activity is correlated with its phosphorylation state.,online information:APC entry,online information:Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) website,online information:Information about APC mutations,online information:The Singapore human mutation and polymorphism database,PTM:Phosphorylated by GSK3B.,PTM:Ubiquitinated, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. Ubiquitination is facilitated by Axin. Deubiquitinated by ZRANB1/TRABID.,similarity:Belongs to the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) family.,similarity:Contains 7 ARM repeats.,subunit:Forms homooligomers. Interacts with DIAPH1 and DIAPH2 (By similarity). Interacts with PDZ domains of DLG1 and DLG3. Associates with catenins. Binds axin. Interacts with the N-terminus of ARHGEF4, and the C-terminus of MAPRE1, MAPRE2 and MAPRE3. Found in a complex consisting of ARHGEF4, APC and CTNNB1. Interacts with APC2.,tissue specificity:Expressed in a variety of tissues.,
研究领域
WNT;WNT-T CELLRegulates Actin and Cytoskeleton;Pathways in cancer;Colorectal cancer;Endometrial cancer;Basal cell carcinoma;