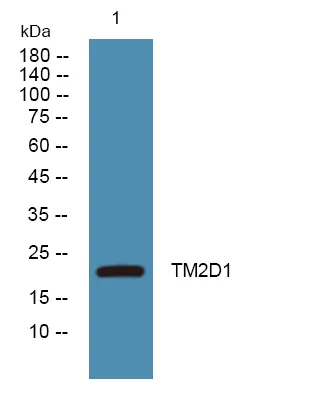
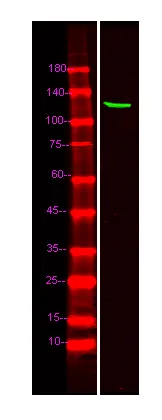
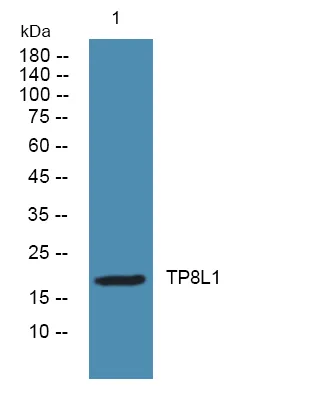
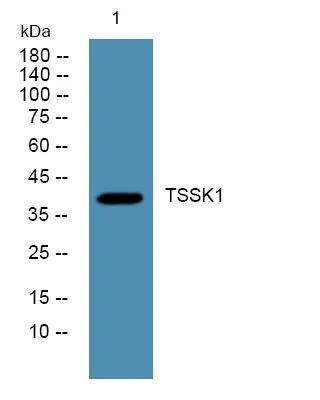
产品概述
产品性能
免疫原
产品应用
研究背景
This gene encodes a member of the gap junction protein family. The gap junctions were first characterized by electron microscopy as regionally specialized structures on plasma membranes of contacting adherent cells. These structures were shown to consist of cell-to-cell channels that facilitate the transfer of ions and small molecules between cells. The gap junction proteins, also known as connexins, purified from fractions of enriched gap junctions from different tissues differ. According to sequence similarities at the nucleotide and amino acid levels, the gap junction proteins are divided into two categories, alpha and beta. Mutations in this gene are responsible for as much as 50% of pre-lingual, recessive deafness. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008],disease:Defects in GJB2 are a cause of keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome (KID syndrome) [MIM:148210]; an autosomal dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia. Ectodermal dysplasias (EDs) constitute a heterogeneous group of developmental disorders affecting tissues of ectodermal origin. EDs are characterized by abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures such as hair, teeth, nails and sweat glands, with or without any additional clinical sign. Each combination of clinical features represents a different type of ectodermal dysplasia. KID syndrome is characterized by the association of hyperkeratotic skin lesions with vascularizing keratitis and profound sensorineural hearing loss. Clinical features include deafness, ichthyosis, photobia, absent or decreased eyebrows, sparse or absent scalp hair, decreased sweating and dysplastic finger and toenails.,disease:Defects in GJB2 are a cause of palmoplantar keratoderma with deafness (PPKDFN) [MIM:148350]. PPKDFN is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the association of palmoplantar hyperkeratosis with progressive, bilateral, high-frequency, sensorineural deafness.,disease:Defects in GJB2 are a cause of Vohwinkel syndrome (VS) [MIM:124500]. VS is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by hyperkeratosis, constriction on finger and toes and congenital deafness.,disease:Defects in GJB2 are the cause of Bart-Pumphrey syndrome (BPS) [MIM:149200]. BPS is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by sensorineural hearing loss, palmoplantar keratoderma, knuckle pads, and leukonychia, It shows considerable phenotypic variability.,disease:Defects in GJB2 are the cause of ichthyosis hystrix-like with deafness syndrome (HID syndrome) [MIM:602540]. HID syndrome is an autosomal-dominant inherited keratinizing disorder characterized by sensorineural deafness and spiky hyperkeratosis affecting the entire skin. HID syndrome is considered to differ from the similar KID syndrome in the extent and time of occurrence of skin symptoms and the severity of the associated keratitis.,disease:Defects in GJB2 are the cause of non-syndromic sensorineural deafness autosomal dominant type 3A (DFNA3A) [MIM:601544].,disease:Defects in GJB2 are the cause of non-syndromic sensorineural deafness autosomal recessive type 1 (DFNB1) [MIM:220290]. DFNB1 is a form of sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information.,function:One gap junction consists of a cluster of closely packed pairs of transmembrane channels, the connexons, through which materials of low MW diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell.,online information:Gene page,polymorphism:The Thr-34 allele was originally (PubMed:9139825) thought to be a cause of forms of hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness (DFNA3 and DFNB1).,similarity:Belongs to the connexin family. Beta-type (group I) subfamily.,subunit:A connexon is composed of a hexamer of connexins.,
研究领域