产品概述
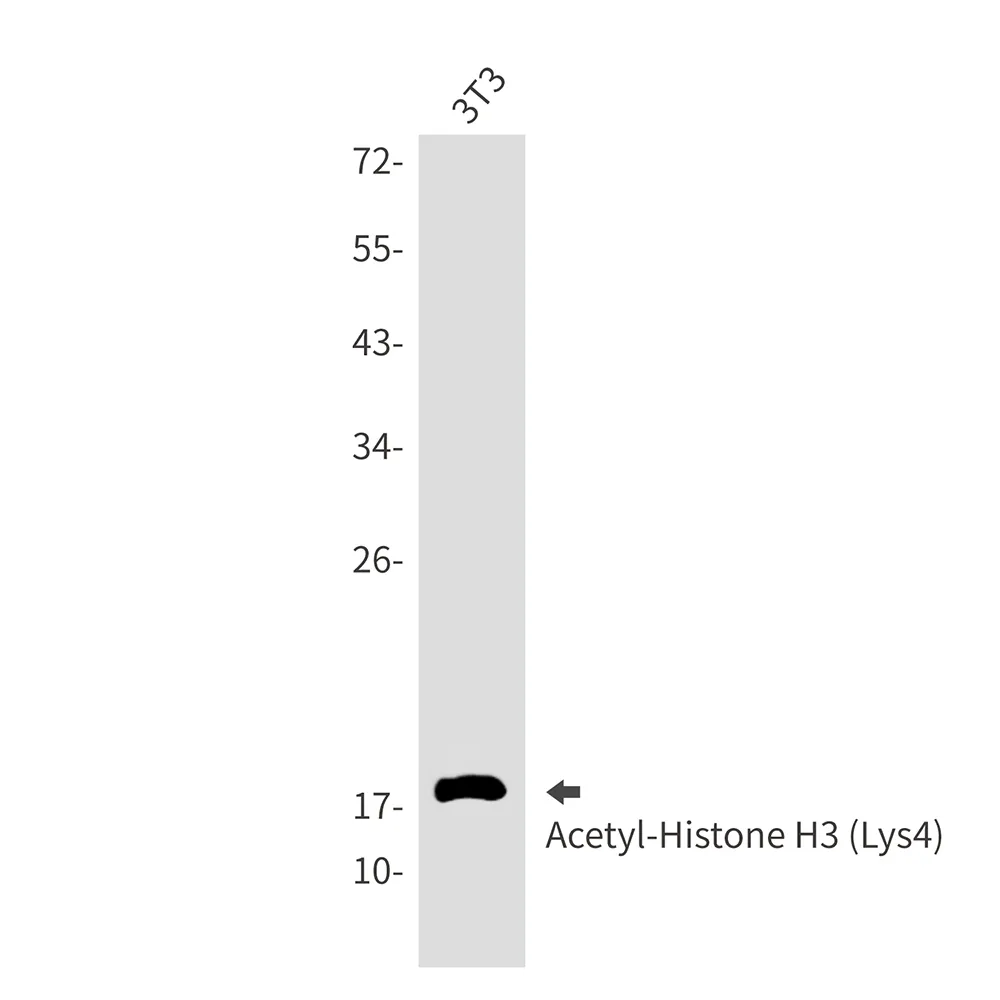
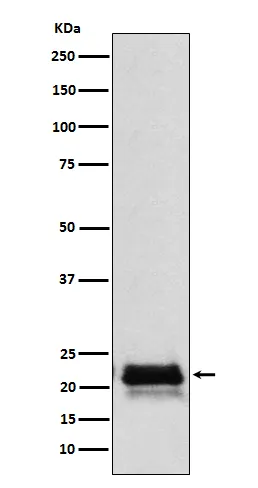
产品性能
免疫原
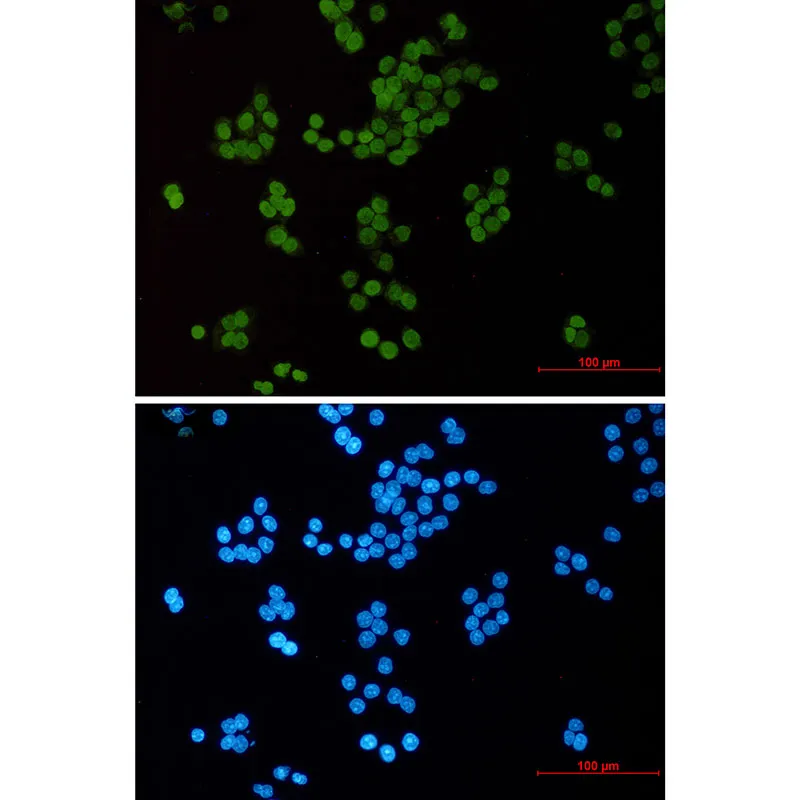
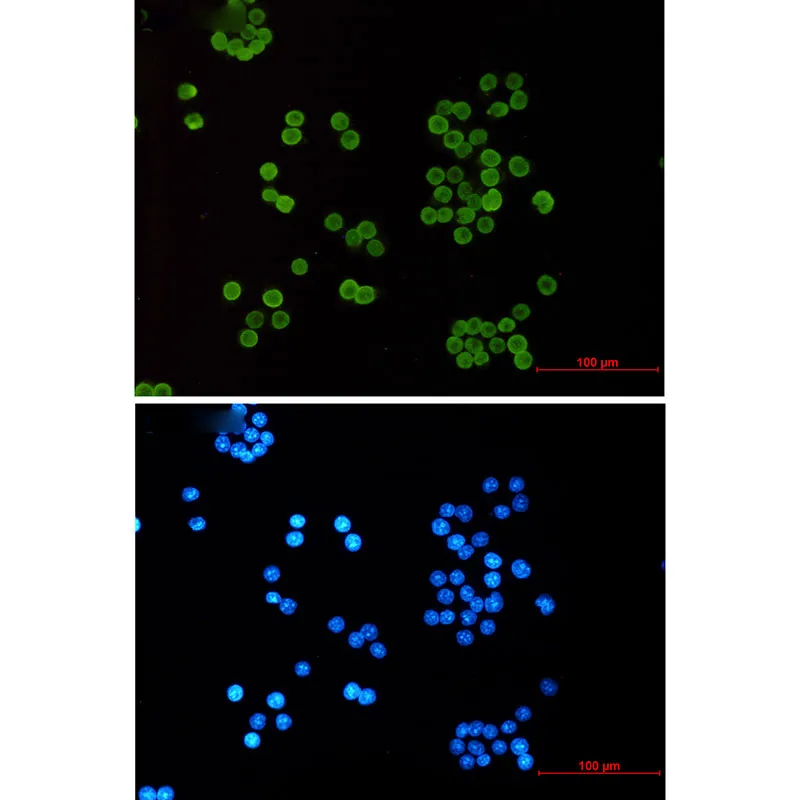
产品应用
研究背景
The protein encoded by this gene is a single stranded DNA-binding protein that binds to multiple DNA elements, including the far upstream element (FUSE) located upstream of c-myc. Binding to FUSE occurs on the non-coding strand, and is important to the regulation of c-myc in undifferentiated cells. This protein contains three domains, an amphipathic helix N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding central domain, and a C-terminal transactivation domain that contains three tyrosine-rich motifs. The N-terminal domain is thought to repress the activity of the C-terminal domain. This protein is also thought to bind RNA, and contains 3'-5' helicase activity with in vitro activity on both DNA-DNA and RNA-RNA duplexes. Aberrant expression of this gene has been found in malignant tissues, and this gene is important to neural system and lung development. Binding of this protein to viral RNA is thought to play a role in several viral diseases, including hepatitis C and hand, foot and mouth disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]
研究领域