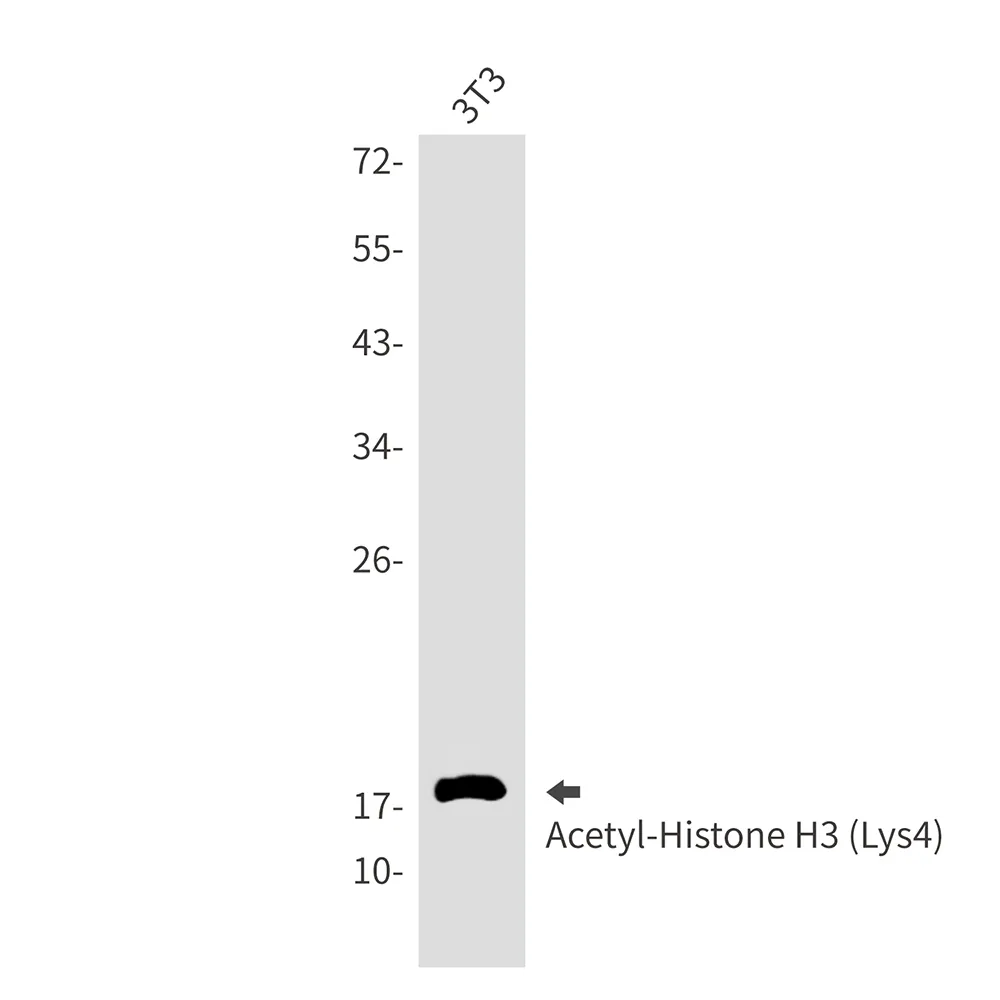
产品概述
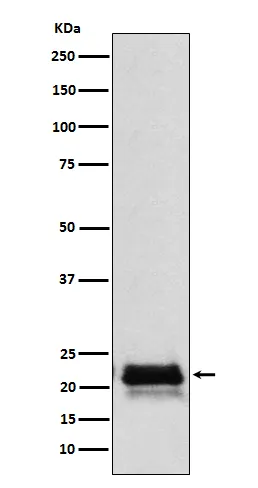
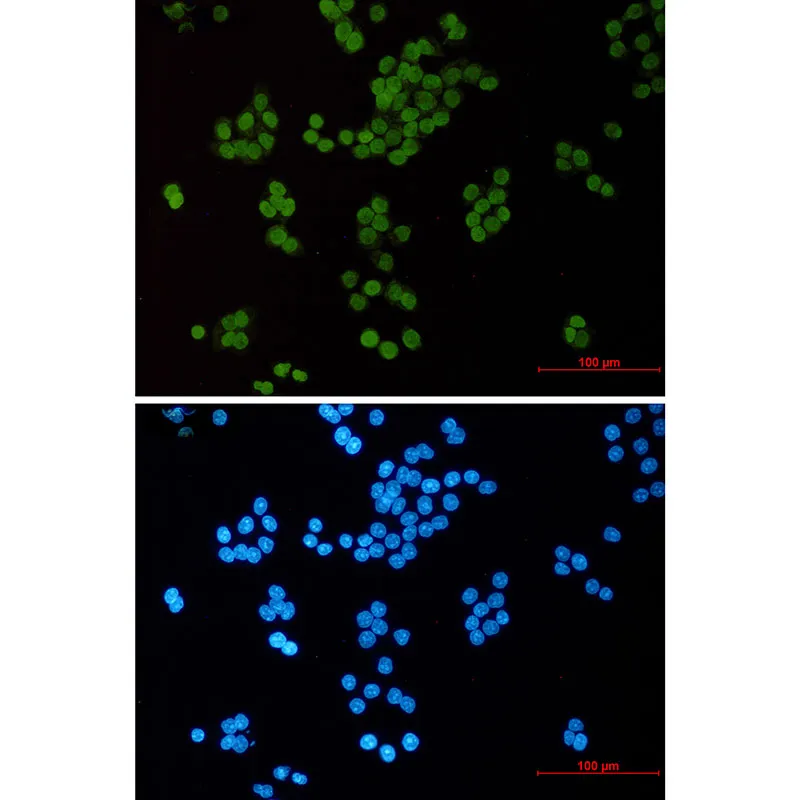
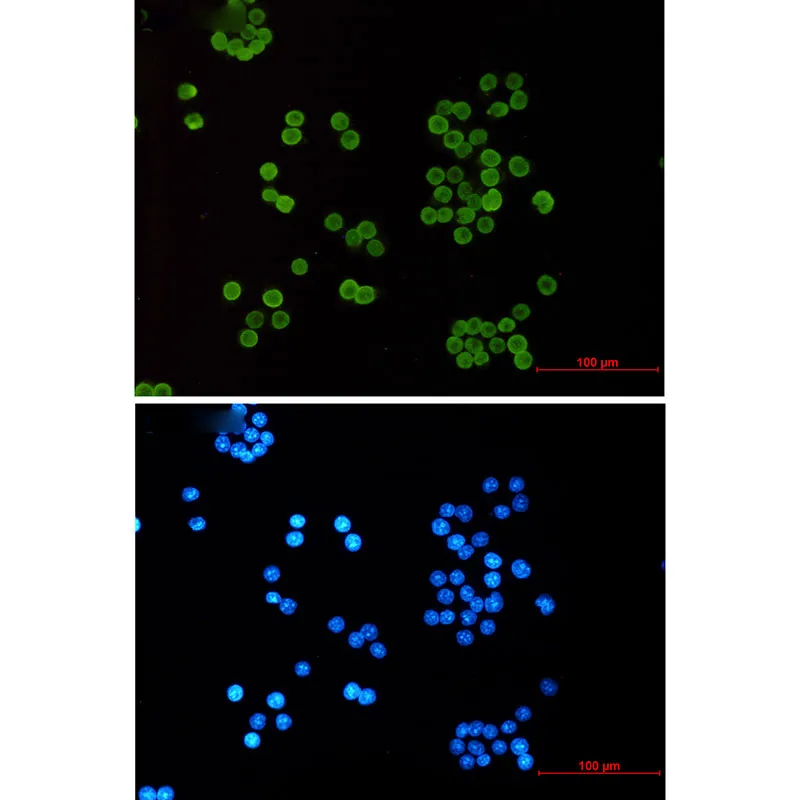
产品性能
免疫原
产品应用
研究背景
Adhesion molecule in postnatal neural development that mediates sialic-acid dependent cell-cell interactions between neuronal and myelinating cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,3-linked sialic acid. Adhesion molecule that mediates interactions between myelinating cells and neurons by binding to neuronal sialic acid- containing gangliosides and to the glycoproteins RTN4R and RTN4RL2 (By similarity). Not required for initial myelination, but seems to play a role in the maintenance of normal axon myelination. Protects motoneurons against apoptosis, also after injury; protection against apoptosis is probably mediated via interaction with neuronal RTN4R and RTN4RL2. Required to prevent degeneration of myelinated axons in adults; this probably depends on binding to gangliosides on the axon cell membrane (By similarity). Negative regulator of neurite outgrowth; in dorsal root ganglion neurons the inhibition is mediated primarily via binding to neuronal RTN4R or RTN4RL2 and to a lesser degree via binding to neuronal gangliosides. In cerebellar granule cells the inhibition is mediated primarily via binding to neuronal gangliosides. In sensory neurons, inhibition of neurite extension depends only partially on RTN4R, RTN4RL2 and gangliosides. Inhibits axon longitudinal growth (By similarity). Inhibits axon outgrowth by binding to RTN4R (By similarity). Preferentially binds to alpha-2,3-linked sialic acid. Binds ganglioside Gt1b (By similarity).
研究领域
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs);