产品概述
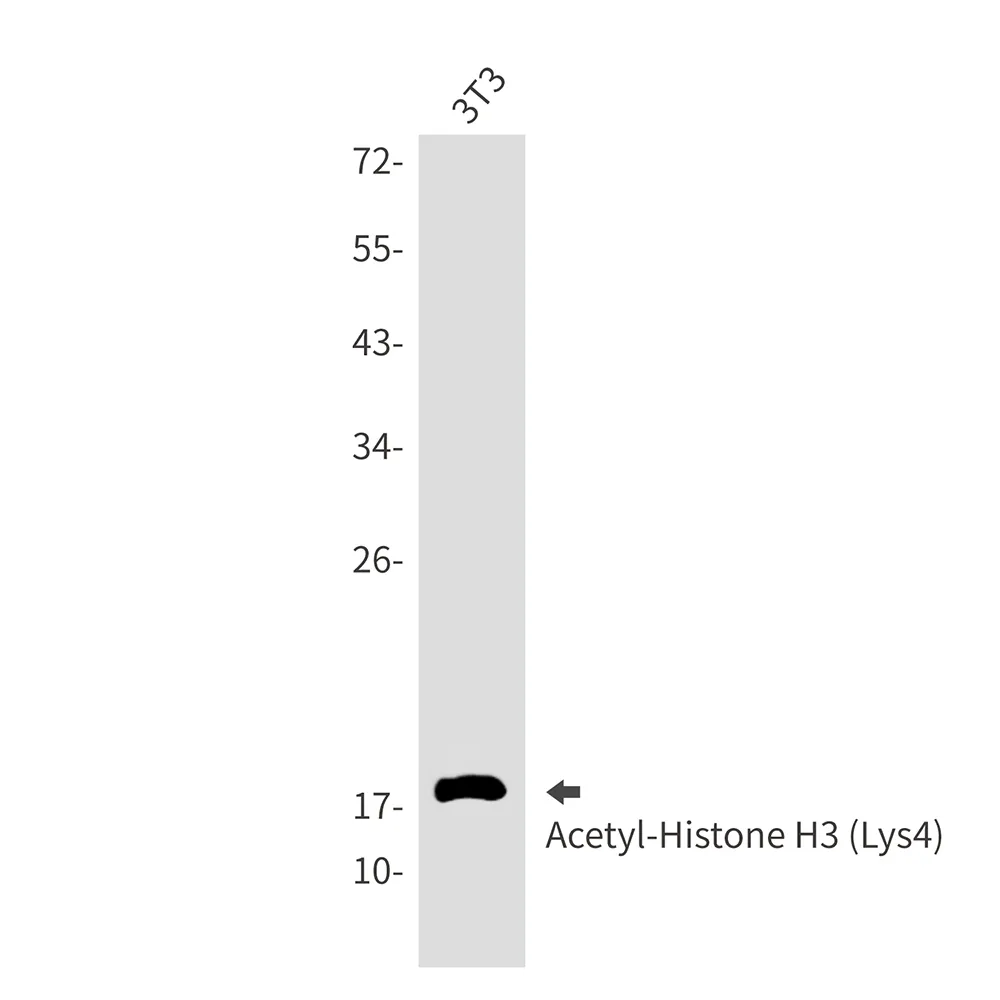
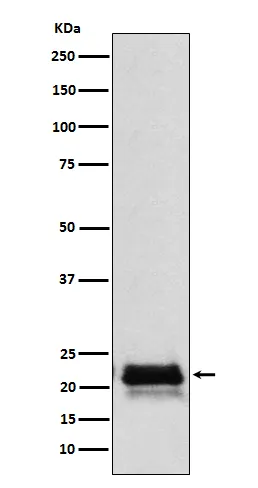
产品性能
免疫原
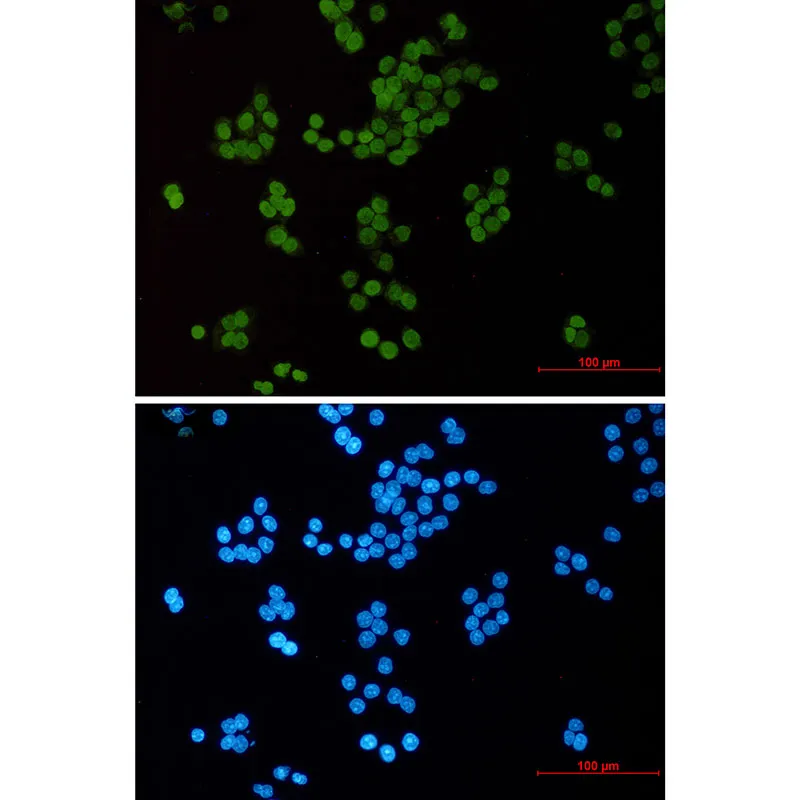
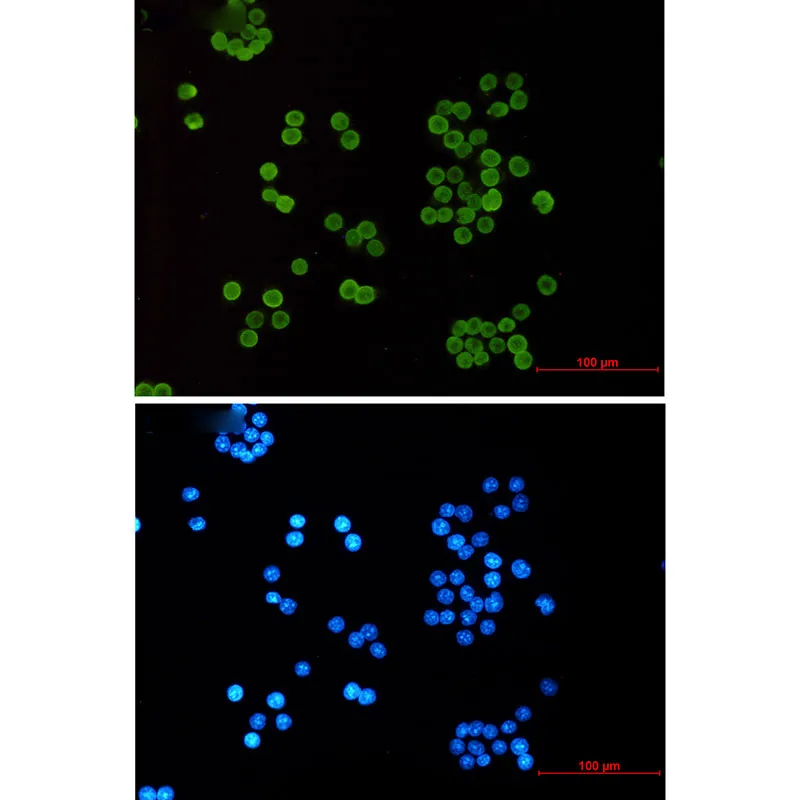
产品应用
研究背景
Severs microtubules in vitro in an ATP-dependent manner. This activity may promote rapid reorganization of cellular microtubule arrays, such as during disassembly of interphase microtubules at the G2-M transition. Catalytic subunit of a complex which severs microtubules in an ATP-dependent manner. Microtubule severing may promote rapid reorganization of cellular microtubule arrays and the release of microtubules from the centrosome following nucleation. Microtubule release from the mitotic spindle poles may allow depolymerization of the microtubule end proximal to the spindle pole, leading to poleward microtubule flux and poleward motion of chromosome. Microtubule release within the cell body of neurons may be required for their transport into neuronal processes by microtubule-dependent motor proteins. This transport is required for axonal growth.
研究领域
Cell Biology