产品概述
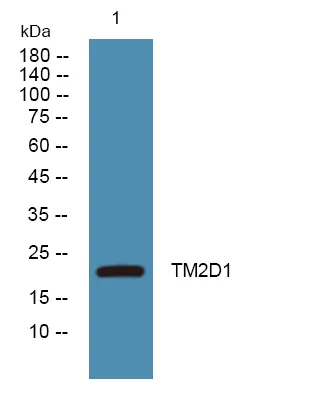
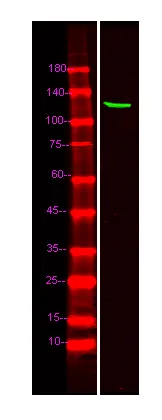
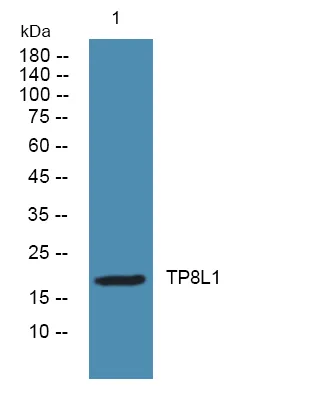
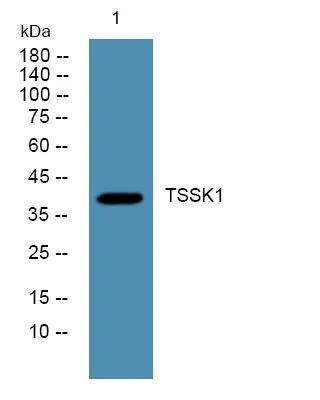
产品性能
免疫原
产品应用
研究背景
This gene encodes a DNA-binding protein that is important in transcription-coupled excision repair. The encoded protein has ATP-stimulated ATPase activity, interacts with several transcription and excision repair proteins, and may promote complex formation at DNA repair sites. Mutations in this gene are associated with Cockayne syndrome type B and cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome 1. Alternative splicing occurs between a splice site from exon 5 of this gene to the 3' splice site upstream of the open reading frame (ORF) of the adjacent gene, piggyback-derived-3 (GeneID:267004), which activates the alternative polyadenylation site downstream of the piggyback-derived-3 ORF. The resulting transcripts encode a fusion protein that shares sequence with the product of each individual gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016],disease:Defects in ERCC6 are a cause of De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome (DSC) [MIM:278800]; also known as xerodermic idiocy. DSC is an autosomal recessive syndrome consisting of xeroderma pigmentosum associated with mental retardation, retarded growth, gonadal hypoplasia and sometimes neurologic complications.,disease:Defects in ERCC6 are a cause of UV-sensitive syndrome (UVS) [MIM:600630]. UVS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by photosensitivity and mild freckling but without neurological abnormalities or skin tumors.,disease:Defects in ERCC6 are the cause of cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal syndrome type 1 (COFS1) [MIM:214150]; also known as COFS syndrome or Pena-Shokeir syndrome type 2. COFS is a degenerative autosomal recessive disorder of prenatal onset affecting the brain, eye and spinal cord. After birth, it leads to brain atrophy, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, hypotonia, cataracts, microcornea, optic atrophy, progressive joint contractures and growth failure. Facial dysmorphism is a constant feature. Abnormalities of the skull, eyes, limbs, heart and kidney also occur.,disease:Defects in ERCC6 are the cause of Cockayne syndrome type B (CSB) [MIM:133540]. Cockayne syndrome is a rare disorder characterized by cutaneous sensitivity to sunlight, abnormal and slow growth, cachectic dwarfism, progeroid appearance, progressive pigmentary retinopathy and sensorineural deafness. There is delayed neural development and severe progressive neurologic degeneration resulting in mental retardation. Two clinical forms are recognized: in the classical form or Cockayne syndrome type 1, the symptoms are progressive and typically become apparent within the first few years or life; the less common Cockayne syndrome type 2 is characterized by more severe symptoms that manifest prenatally. Cockayne syndrome shows some overlap with certain forms of xeroderma pigmentosum. Unlike xeroderma pigmentosum, patients with Cockayne syndrome do not manifest increased freckling and other pigmentation abnormalities in the skin and have no significant increase in skin cancer.,disease:Genetic variation in ERCC6 is associated with susceptibility to age-related macular degeneration type 5 (ARMD5) [MIM:609413]. ARMD is a multifactorial eye disease and the most common cause of irreversible vision loss in the developed world. In most patients, the disease is manifest as ophthalmoscopically visible yellowish accumulations of protein and lipid (known as drusen) that lie beneath the retinal pigment epithelium and within an elastin-containing structure known as Bruch membrane.,function:Is involved in the preferential repair of active genes. Presumed DNA or RNA unwinding function. Corrects the UV survival and RNA synthesis after UV exposure of Cockayne syndrome complementation group B.,PTM:Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,similarity:Belongs to the SNF2/RAD54 helicase family.,similarity:Contains 1 helicase ATP-binding domain.,similarity:Contains 1 helicase C-terminal domain.,subunit:Interacts with the CSA protein and a subunit of RNA polymerase II TFIIH. Component of the B-WICH complex, at least composed of SMARCA5/SNF2H, BAZ1B/WSTF, SF3B1, DEK, MYO1C, ERCC6, MYBBP1A and DDX21.,
研究领域
Nucleotide excision repair;