产品概述
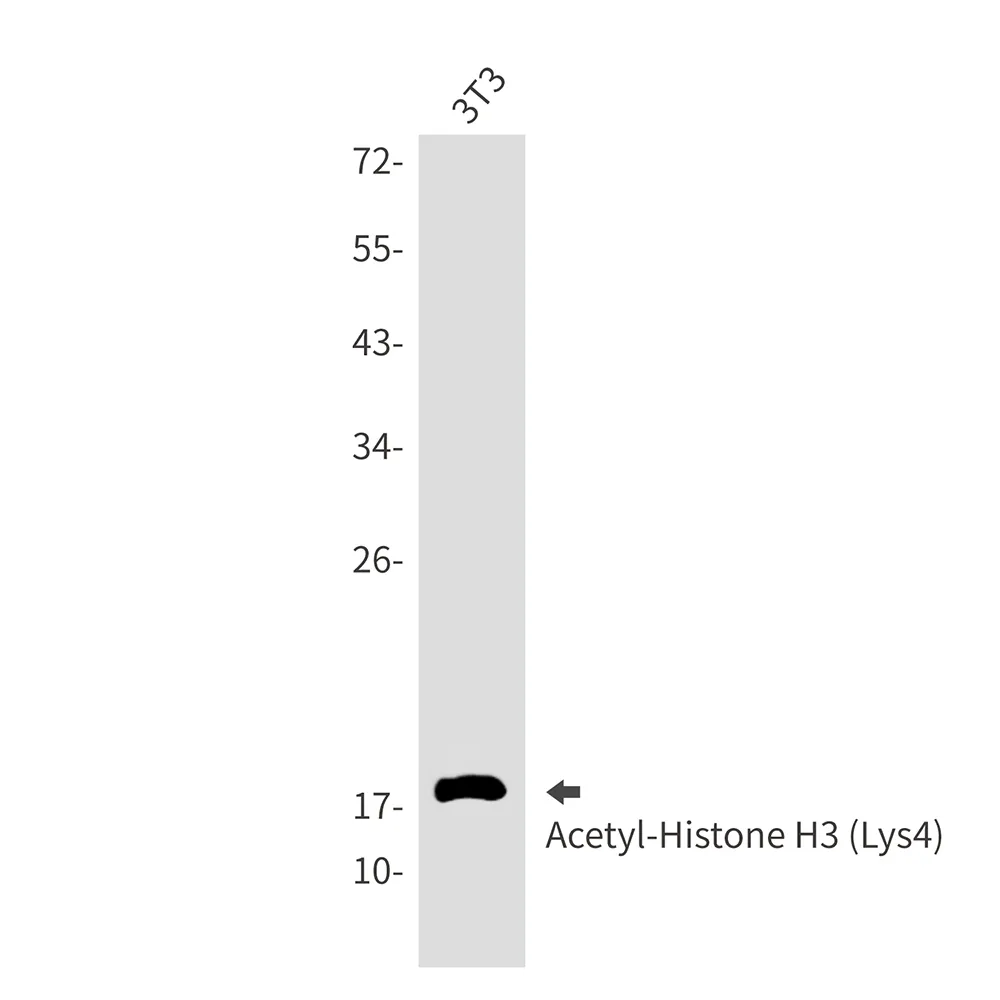
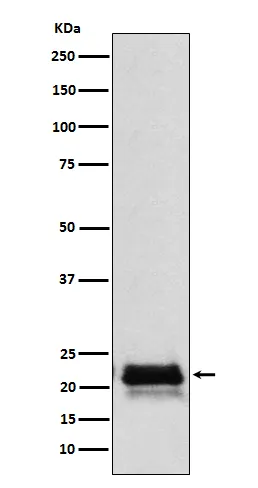
产品性能
免疫原
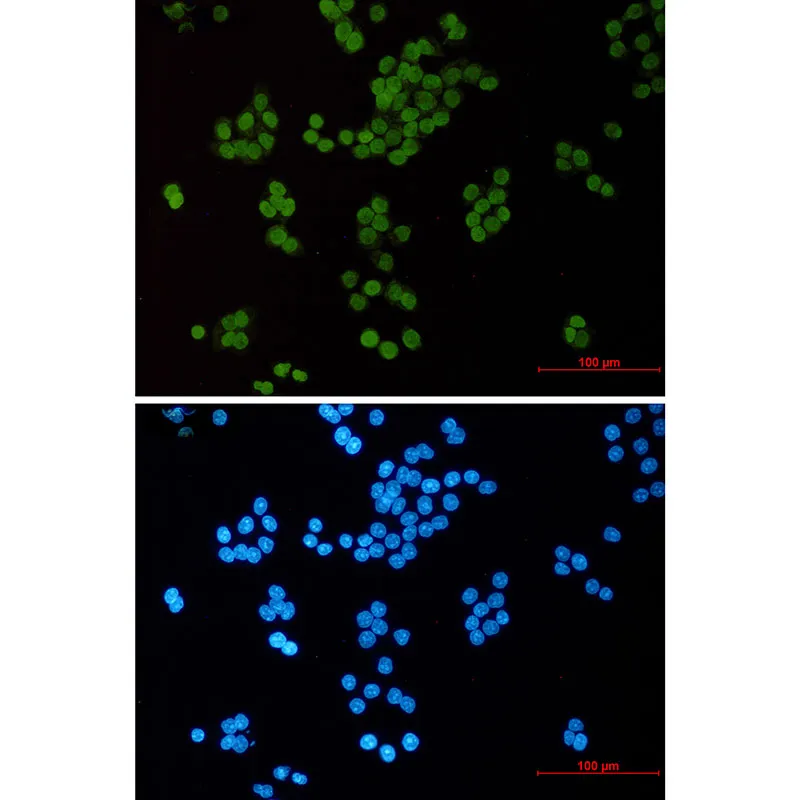
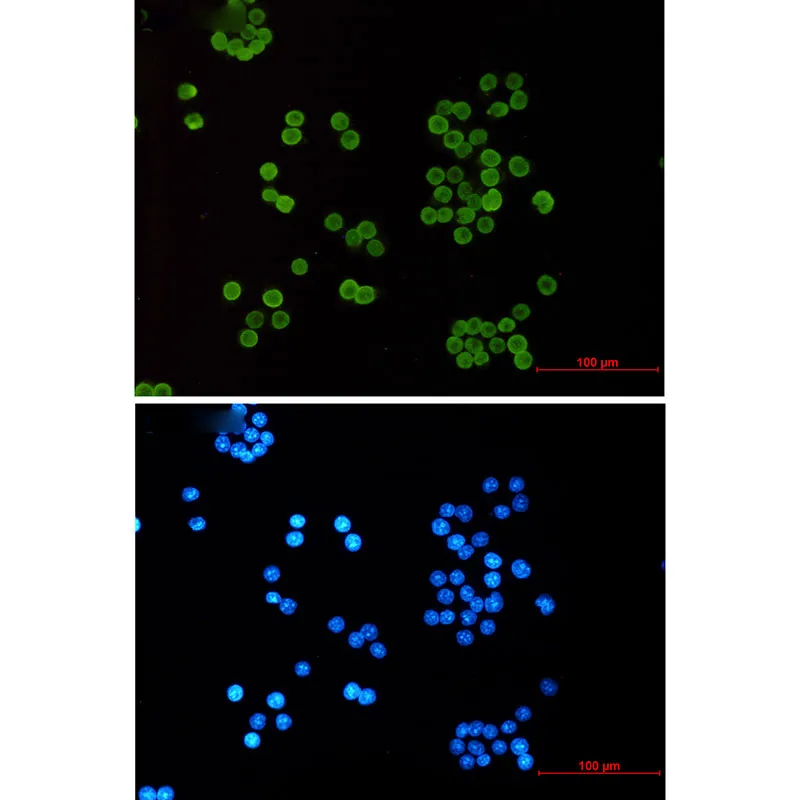
产品应用
研究背景
Flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMO) are an important class of drug-metabolizing enzymes that catalyze the NADPH-dependent oxygenation of various nitrogen-,sulfur-, and phosphorous-containing xenobiotics such as therapeutic drugs, dietary compounds, pesticides, and other foreign compounds. The human FMO gene family is composed of 5 genes and multiple pseudogenes. FMO members have distinct developmental- and tissue-specific expression patterns. The expression of this FMO3 gene, the major FMO expressed in adult liver, can vary up to 20-fold between individuals. This inter-individual variation in FMO3 expression levels is likely to have significant effects on the rate at which xenobiotics are metabolised and, therefore, is of considerable interest to the pharmaceutical industry. This transmembrane protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum of many tissues. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Mutations in this gene cause the disorder trimethylaminuria (TMAu) which is characterized by the accumulation and excretion of unmetabolized trimethylamine and a distinctive body odor. In healthy individuals, trimethylamine is primarily converted to the non odorous trimethylamine N-oxide.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]