产品概述
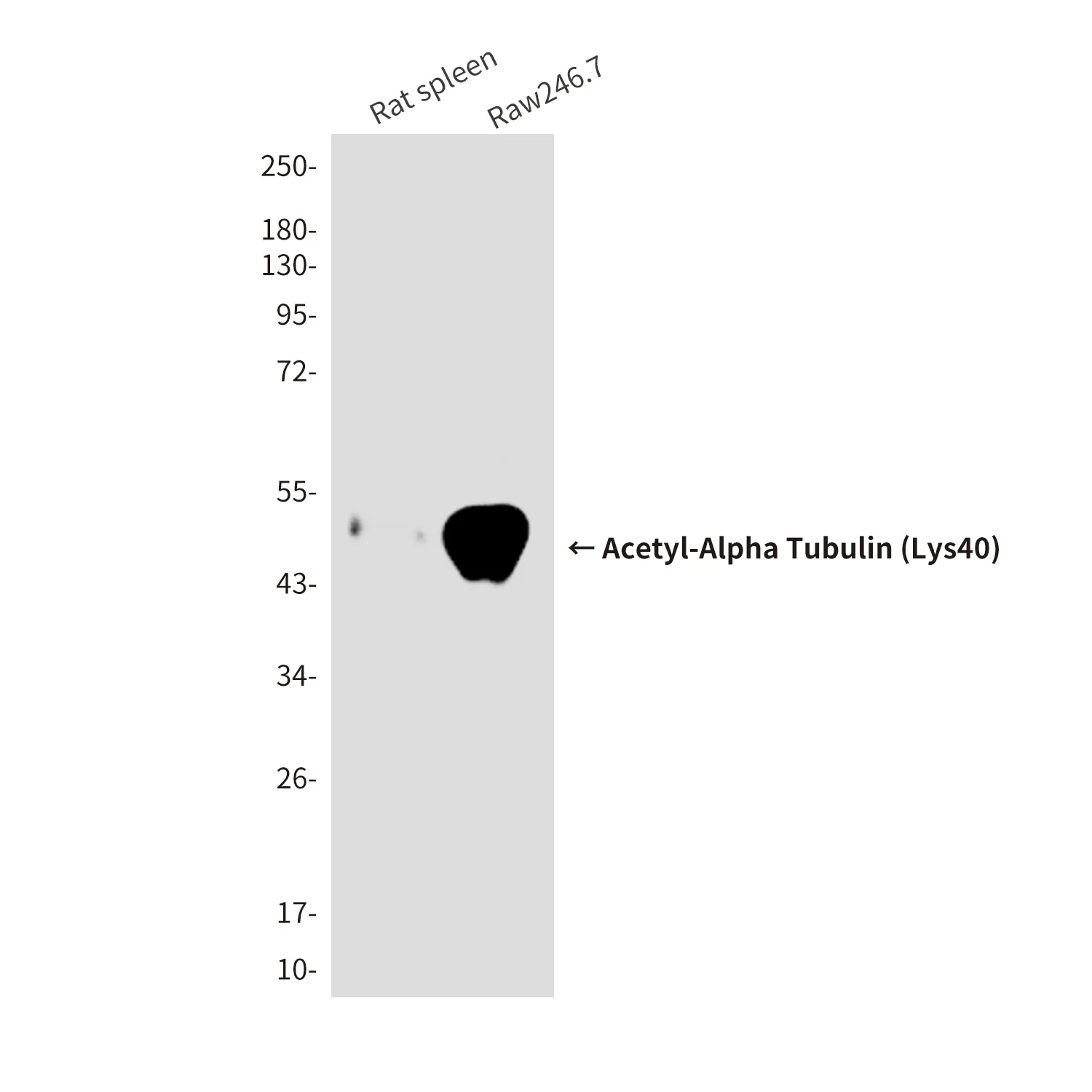
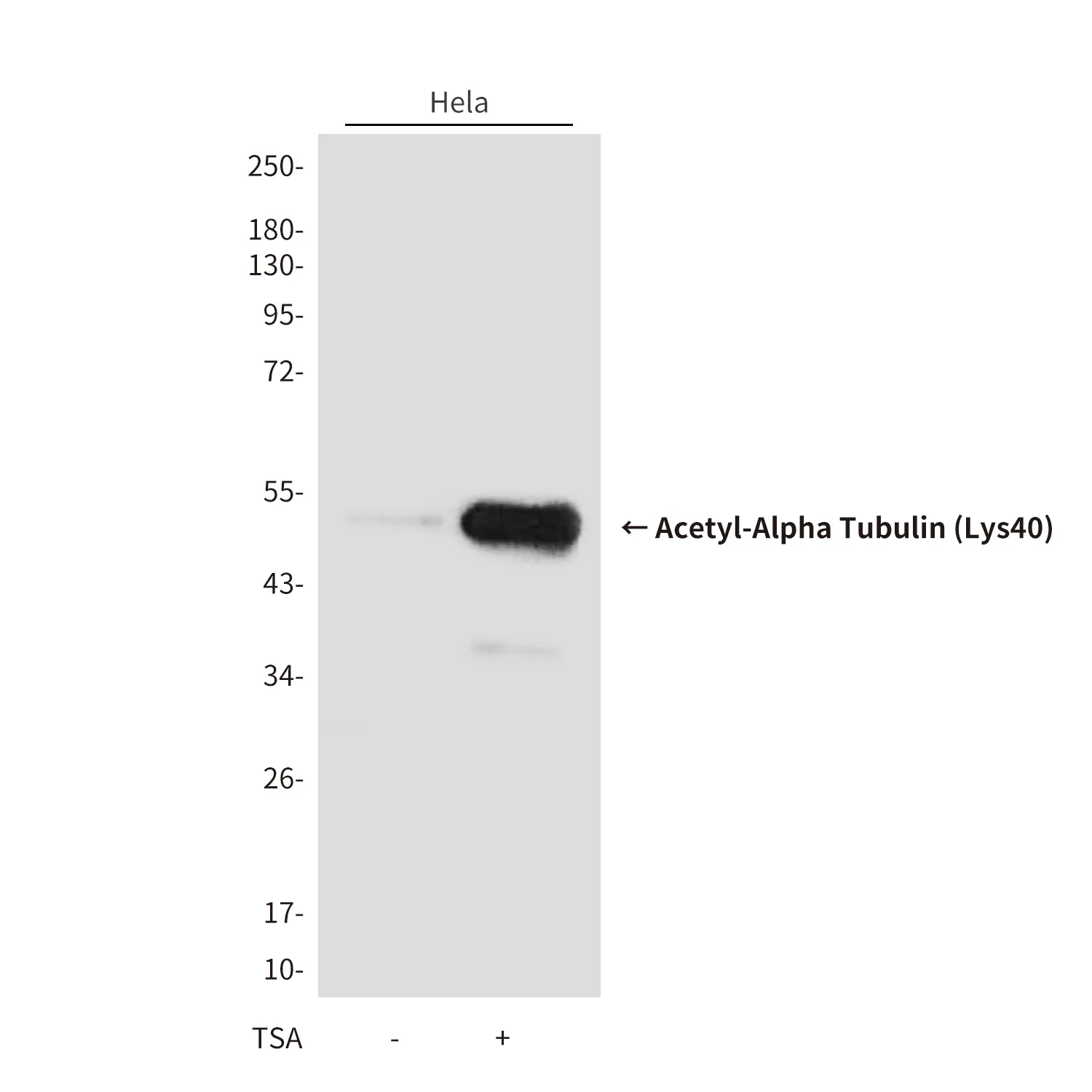
产品性能
免疫原
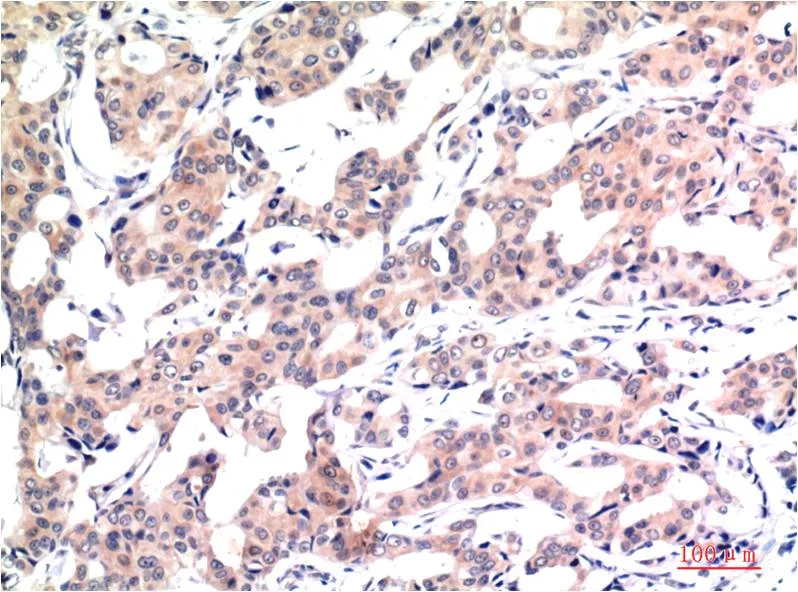
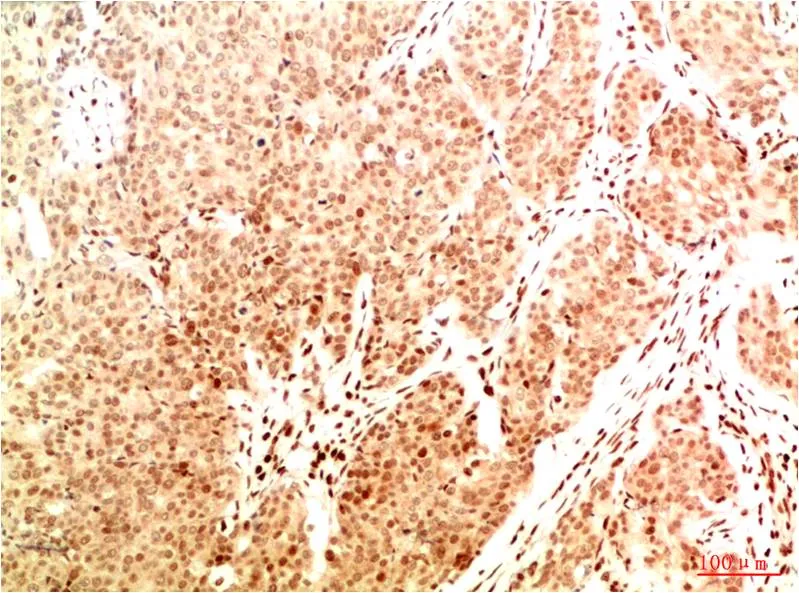
产品应用
研究背景
The protein CD80 (Cluster of Differentiation 80) is a molecule found on activated B cells and monocytes which provides a costimulatory signal necessary for T cell activation and survival. It is also known as B7.1. Its principal mode of action is by binding to CD28. Along with CD86, these molecules provide the necessary stimuli to prime T cells against antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells. CD80 and CD86 also bind to CTLA-4, a cell surface molecule expressed on activated T cells. Interactions between CD80 or CD86 with CTLA-4 decrease the response of T cells. Mouse research by scientists at Emory University showed that estrogen-related bone loss is linked to recently discovered pathways involving various proteins, such as CD80 and other functions. In a nutshell, reactive oxygen stimulates dendritic cells, which activate other immune cells to up-regulate production of CD80, the molecule co-responsible for T cell activation. "When this pathway is activated, it leads to increased T cell TNF production and ultimately to bone loss." In turn, T cells produce a protein, Tumor Necrosis Factor, which increases the formation of osteoclasts in rodents and humans. Osteoclasts cause minerals to be released from the bone, so that calcium is taken into the bloodstream to be used for other functions of the body. Osteoclast differentiation is inhibited by osteoprotegerin; Estrogen stimulates osteoprotegerin production.
研究领域
TGF-beta signaling pathway