产品概述
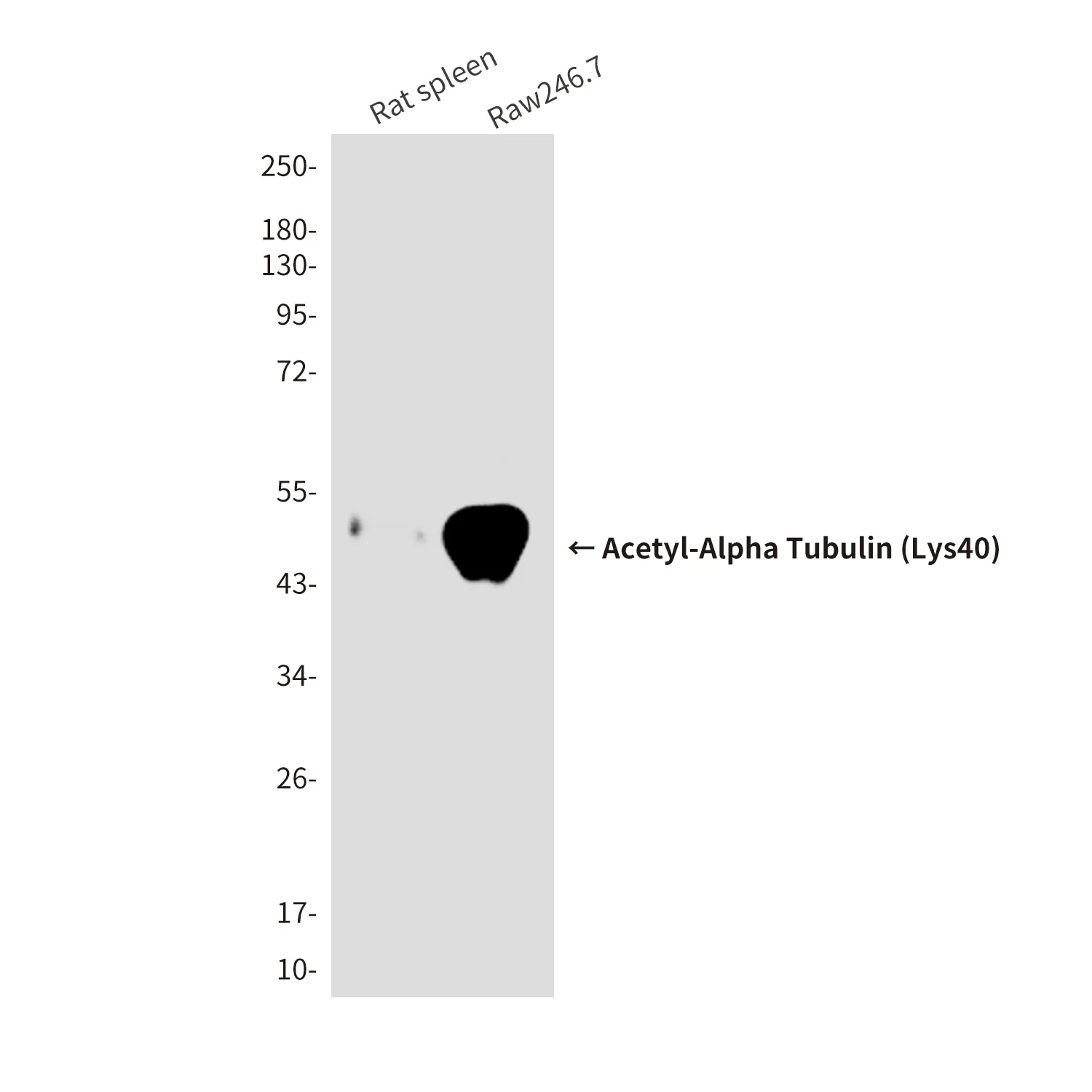
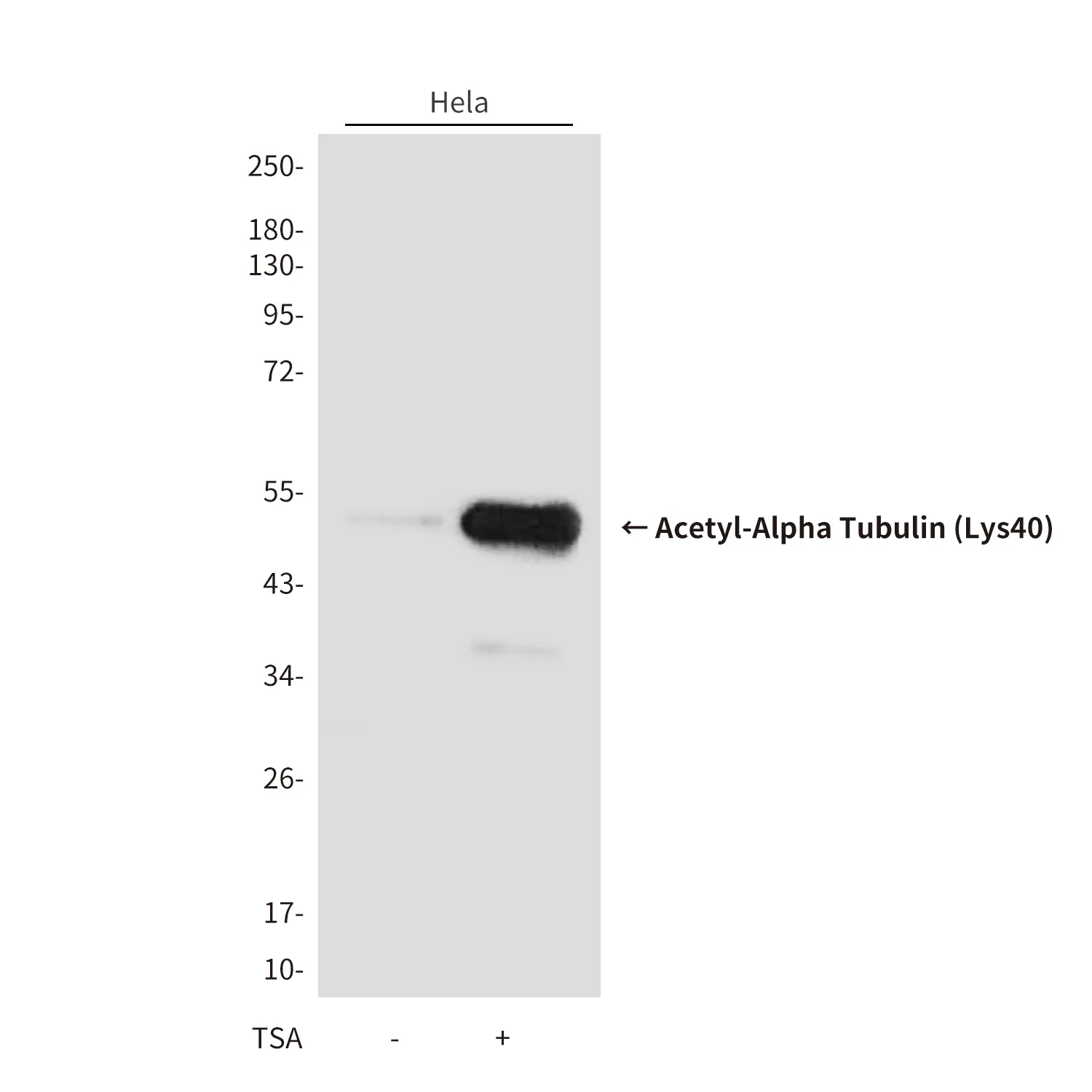
产品性能
免疫原
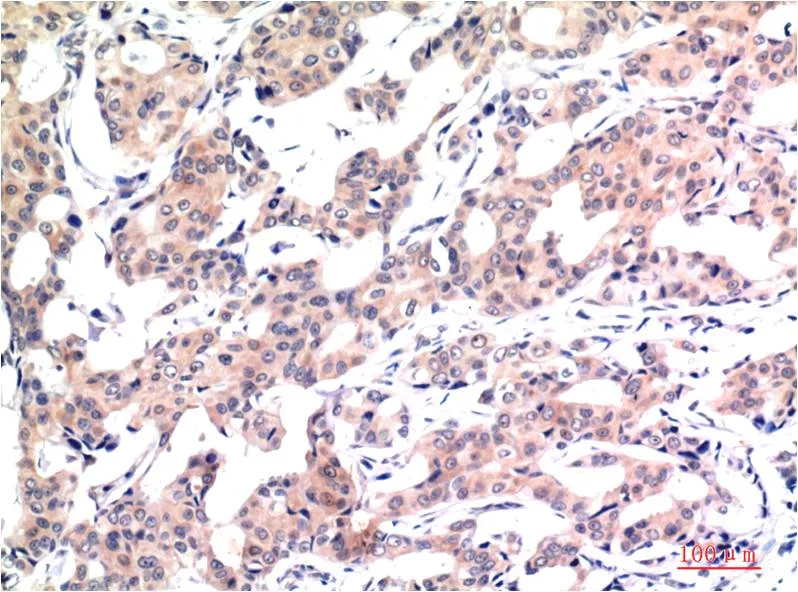
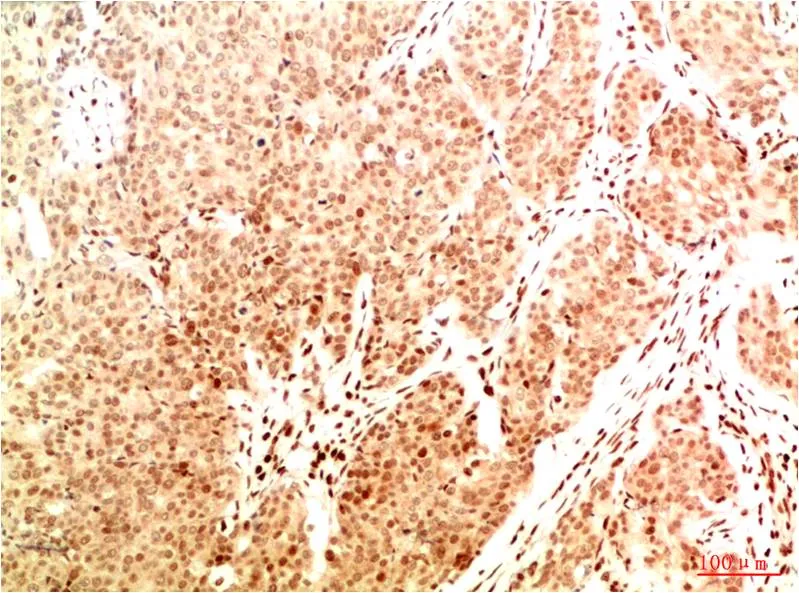
产品应用
研究背景
RAN (ras-related nuclear protein) is a small GTP binding protein belonging to the RAS superfamily that is essential for the translocation of RNA and proteins through the nuclear pore complex. The RAN protein is also involved in control of DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression. Nuclear localization of RAN requires the presence of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1). Mutations in RAN disrupt DNA synthesis. Because of its many functions, it is likely that RAN interacts with several other proteins. RAN regulates formation and organization of the microtubule network independently of its role in the nucleus-cytosol exchange of macromolecules. RAN could be a key signaling molecule regulating microtubule polymerization during mitosis. RCC1 generates a high local concentration of RAN-GTP around chromatin which, in turn, induces the local nucleation of microtubules. RAN is an androgen receptor (AR) coactivator that binds differentially with different lengths of polyglutamine within the androgen receptor. Polyglutamine repeat expansion in the AR is linked to Kennedy's disease (X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy). RAN coactivation of the AR diminishes with polyglutamine expansion within the AR, and this weak coactivation may lead to partial androgen insensitivity during the development of Kennedy's disease.
研究领域